In Nicaragua, Forests and Indigenous Communities Face Threats
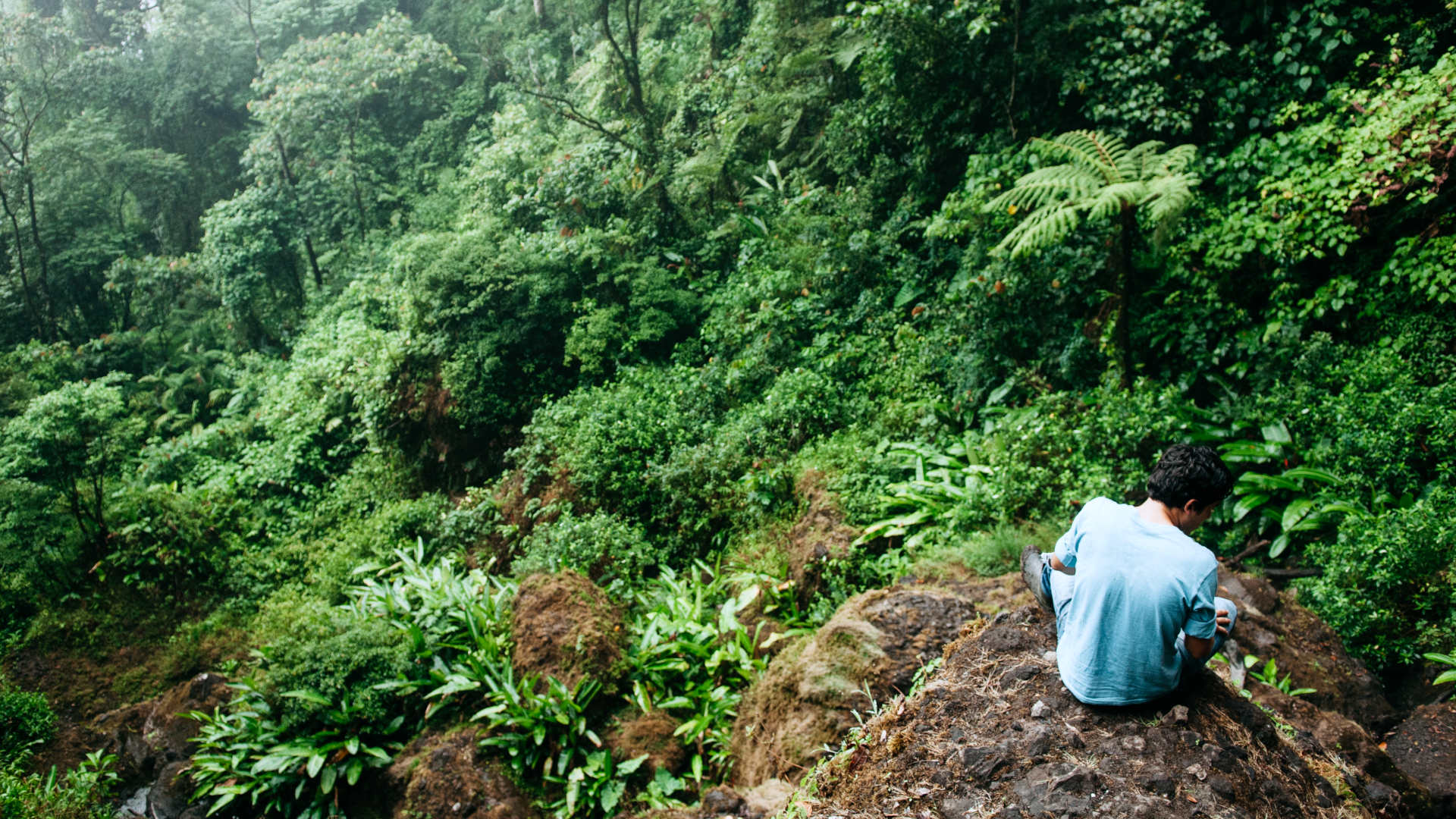
When Juan Carlos Ocampo, an Indigenous community leader in Nicaragua, was a child, deer regularly passed his home as they moved between dense riparian forests on the country’s northern Caribbean coast. Like others in his Miskito community, his family caught fish and crayfish from the rivers, hunted deer and large guinea pig-like paca, and used trees harvested from the forest to build their homes and boats.
Today, he says it’s not possible to hunt, fish, or harvest wood in his community. “It’s very painful to see the destruction of the forest,” he says.
In the past 30 years, swaths of Nicaragua’s vast Caribbean forests have been destroyed by settlers clearing land for agriculture, ranchers pasturing cattle, and loggers harvesting precious wood. Waterways have been contaminated by gold mining and damaging fishing practices. The transformation has intensified in recent years, with increasingly deadly conflicts between settlers and Indigenous communities and 23 percent of Nicaragua’s humid primary forest lost from 2002 to 2019, according to the Global Forest Watch initiative of the World Resources Institute, a sustainability-focused nonprofit research organization.
In 2018, protests by retirees and students over authoritarian policies sparked a widespread uprising against President Daniel Ortega’s regime. During months of clashes between dissidents and government forces, hundreds of people were imprisoned and more than 300 were killed. Ortega remained in power via a brutal crackdown on dissent. To date, an estimated 100,000 people have been exiled, including many activists and members of the press.
Since then, Nicaragua’s forests and Indigenous and Afro-descendant communities have been left without independent oversight at a time when poverty and population growth, as well as government policies, are driving migration to Indigenous and protected forest regions. These forests are increasingly vulnerable, even as the central government has received millions of dollars in World Bank-managed funding to protect them.
Nicaragua’s Caribbean region hosts two reserves recognized by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) for their expansive biodiversity. The Bosawás Biosphere Reserve on the northern border with Honduras forms part of the second largest tropical rainforest tract in the Americas after the Amazon, with a diverse mix of ecosystems from pine savannas to cloud forests rising more than 5,000 feet above sea level. On the Costa Rican border to the south, the Río San Juan Biosphere Reserve is a vast expanse of humid evergreen broadleaf forests threaded by rivers and wetlands.
Both reserves include Indigenous territories and are protected areas that restrict or ban settlement and resource extraction. The Bosawás Biosphere Reserve is home to the Mayangna and Miskito peoples, while the Río San Juan is home to the Rama Indigenous group and Creole-speaking Nicaraguans of African descent (also called Kriol).
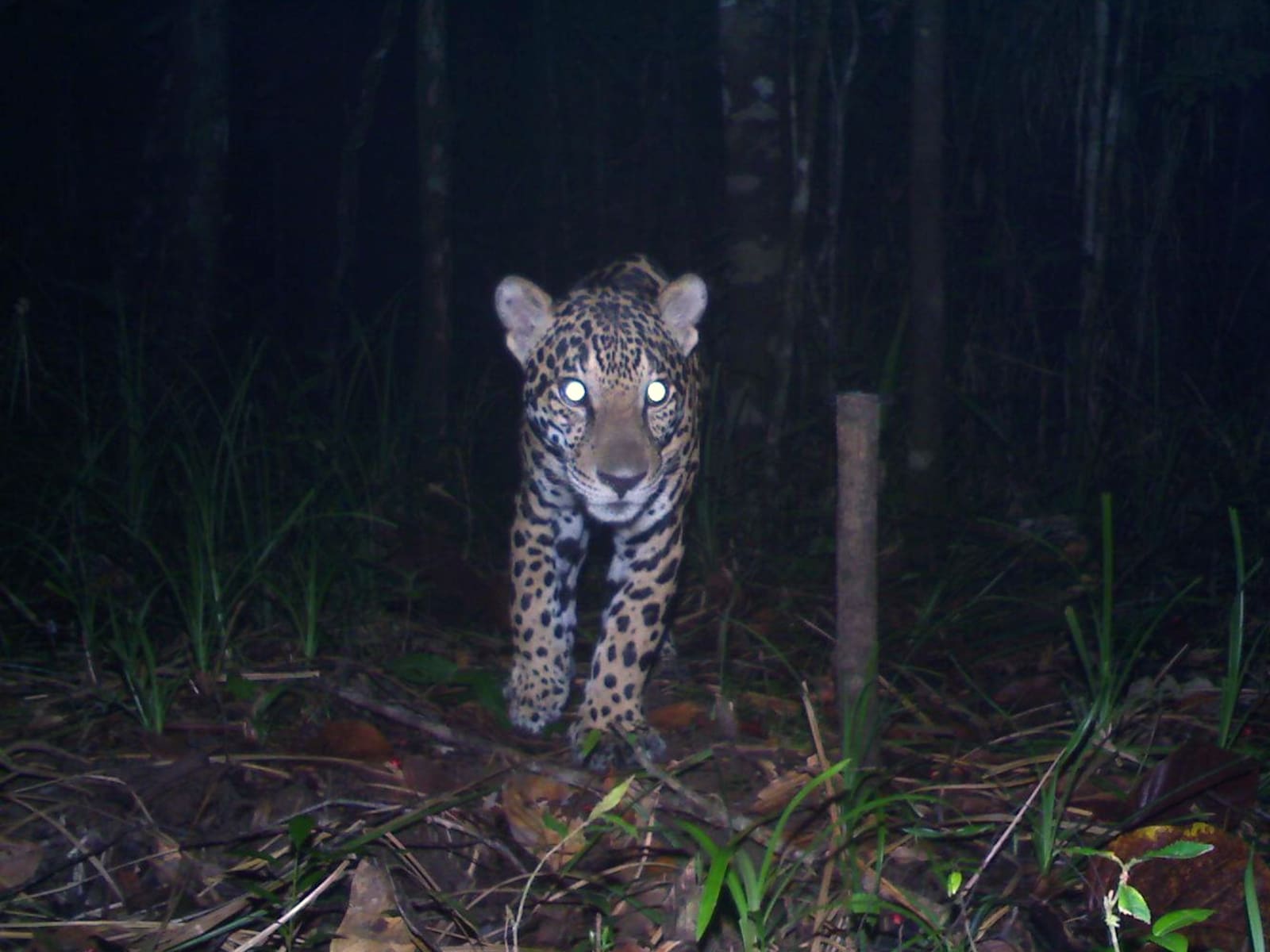
These forests are crucial segments of the increasingly fragmented Mesoamerican biological corridor, which connects habitats in North and South America, allowing the migration of animals like jaguars and providing critical refuge for rare and endangered species. Rafael Reyna-Hurtado, a wildlife ecologist at Mexico’s College of the Southern Border, says the Bosawás, Río San Juan, and other intact Mesoamerican forests are “stepping stones” for animal migration, ensuring genetic diversity among dispersed populations, and resiliency in the event of threats like disease or hurricanes. “We are concerned that these big pieces of forests that are still remaining are losing connectivity,” he says.
Sources: Global Forest Watch; Joel Betts, Global Wildlife ConservationVisual: Aleszu Bajak for Undark
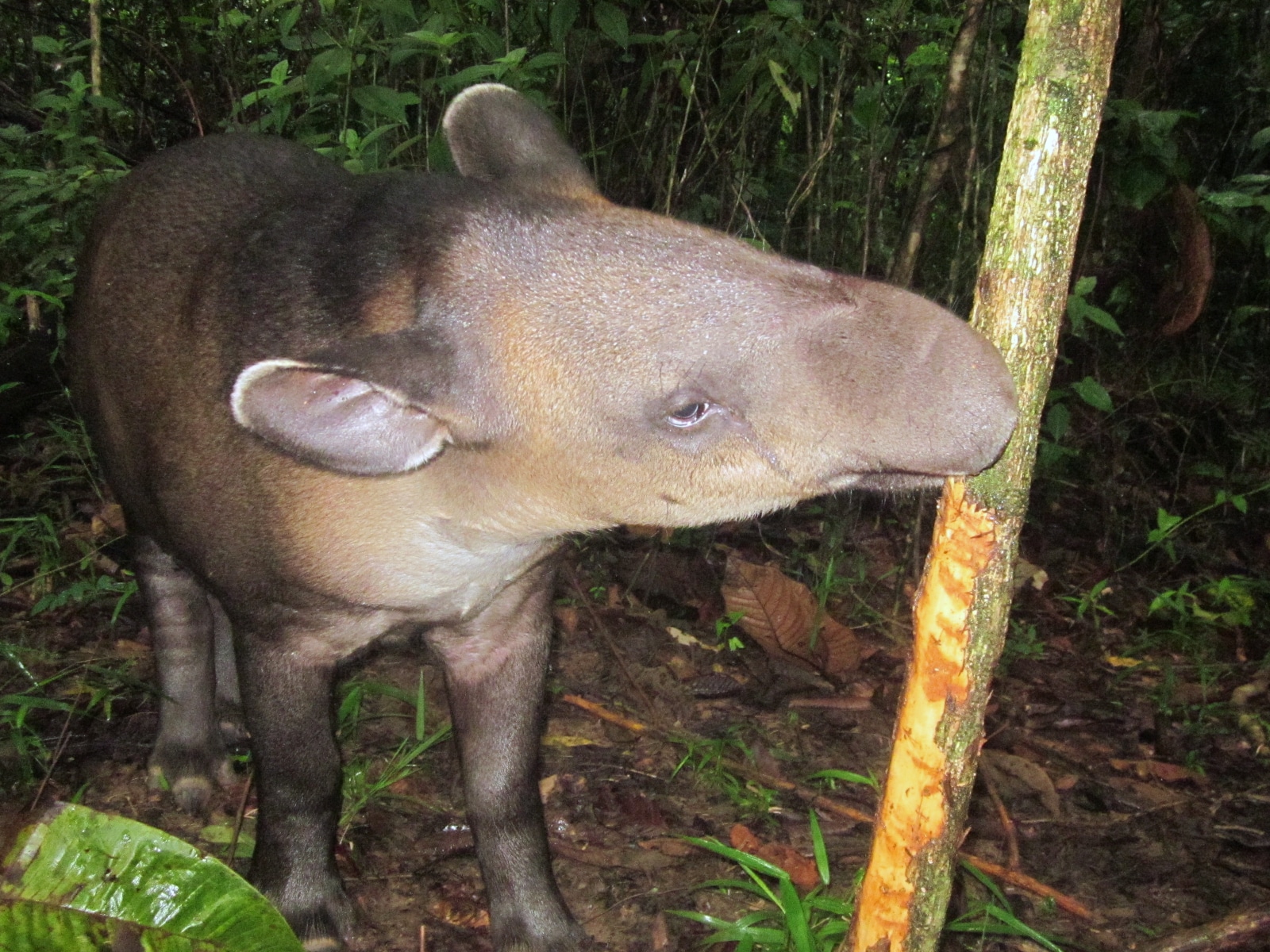
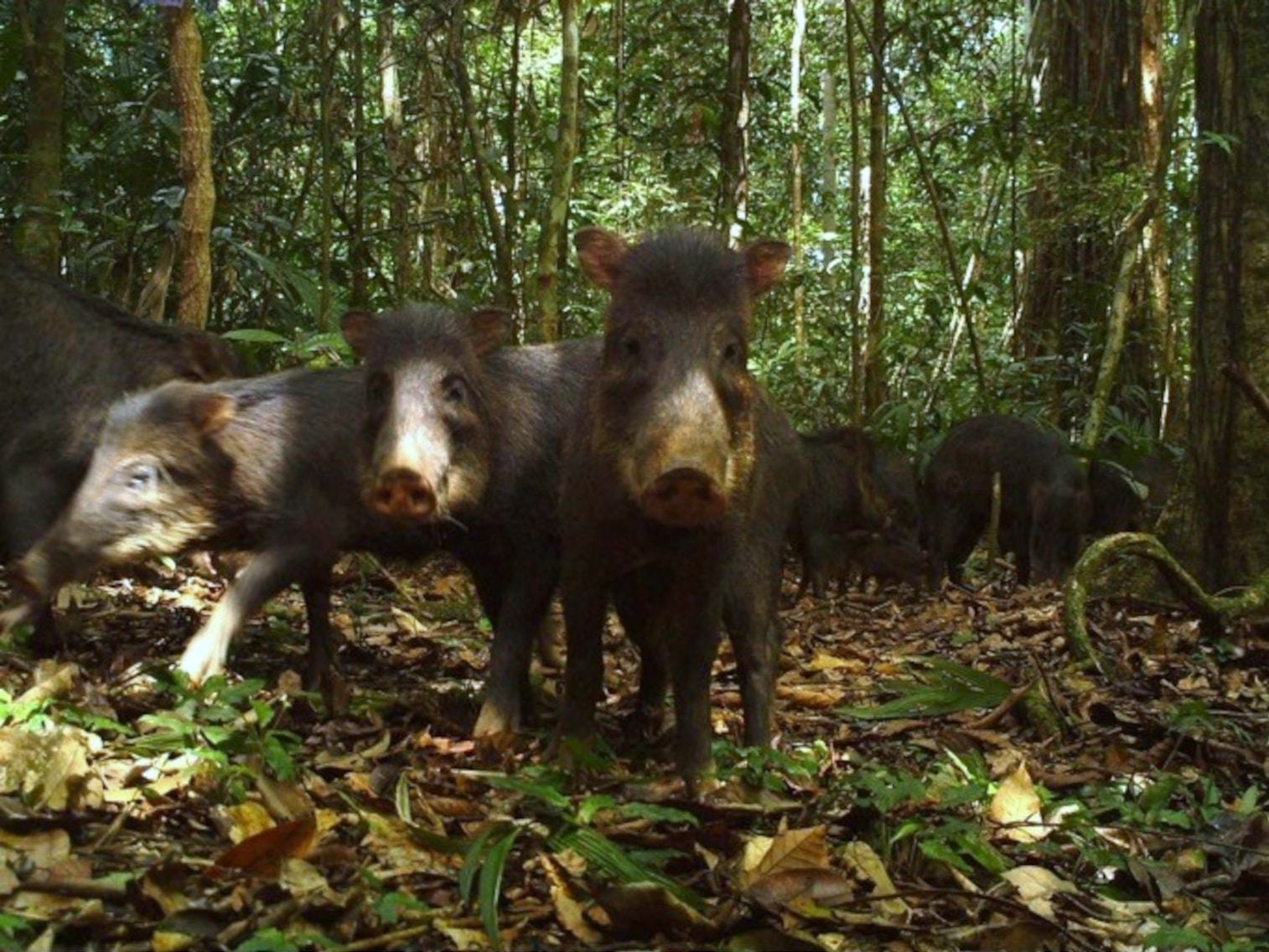
While these forests provide critical habitat for jaguars, large endangered hoofed mammals like peccaries and tapirs are most vulnerable, says Reyna-Hurtado. Unlike jaguars, they’re not able to travel long distances for suitable habitat. They are also more sensitive to human encroachment, preferring undisturbed forests. Tapirs and peccaries perform critical ecosystem services, he explains. Tapirs, sometimes called “gardeners of the forest,” are important seed dispersers since they defecate throughout forest ecosystems, including in water, while the voracious eating habits of peccaries encourage plant diversity.
In a recent study, Reyna-Hurtado and others warned of “precipitous” population declines of white-lipped peccaries in their most critical refuges in Central America, like Bosawás, where “wildlands” with limited human influence have been reduced by 30 percent in the last 15 years.
Armando Dans, a Nicaraguan conservationist with Global Wildlife Conservation, a U.S.-based conservation nonprofit, has seen a dramatic change in the proportion of forest to developed land between the Bosawás and Río San Juan reserves over the last 15 years. “Before, there would be deforested patches. Now it’s the opposite, there are patches of forest in the pastures” and fields, he says. As a result, some species may be unable to move between intact forests, becoming isolated in one reserve or the other.
The Bosawás and the Río San Juan forests are of “vital importance,” says Ivania Andrea Cornejo, an investigator at the Interdisciplinary Institute of Natural Sciences at the Central American University in Nicaragua. In addition to providing connectivity for wildlife, these forests store significant amounts of carbon. “It’s worrying to see the level of deterioration” in Bosawás, she says, and notes Río San Juan had been well-conserved until recently. According to her analysis of data collected by community rangers in Río San Juan, settler activity increased dramatically over the last few years, with observations of camps, homes, clear-cutting, agriculture, and roads doubling to even quadrupling from 2017 to 2019.



A 2017 study by Nicaragua’s Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources (Marena) found poverty, population growth, valuable domestic and export markets for beef, and perceptions of “unused” land were the drivers of migration of landless farmers from mestizo communities (those of mixed European and Indigenous descent), in western regions to Indigenous and protected areas on the Caribbean coast.
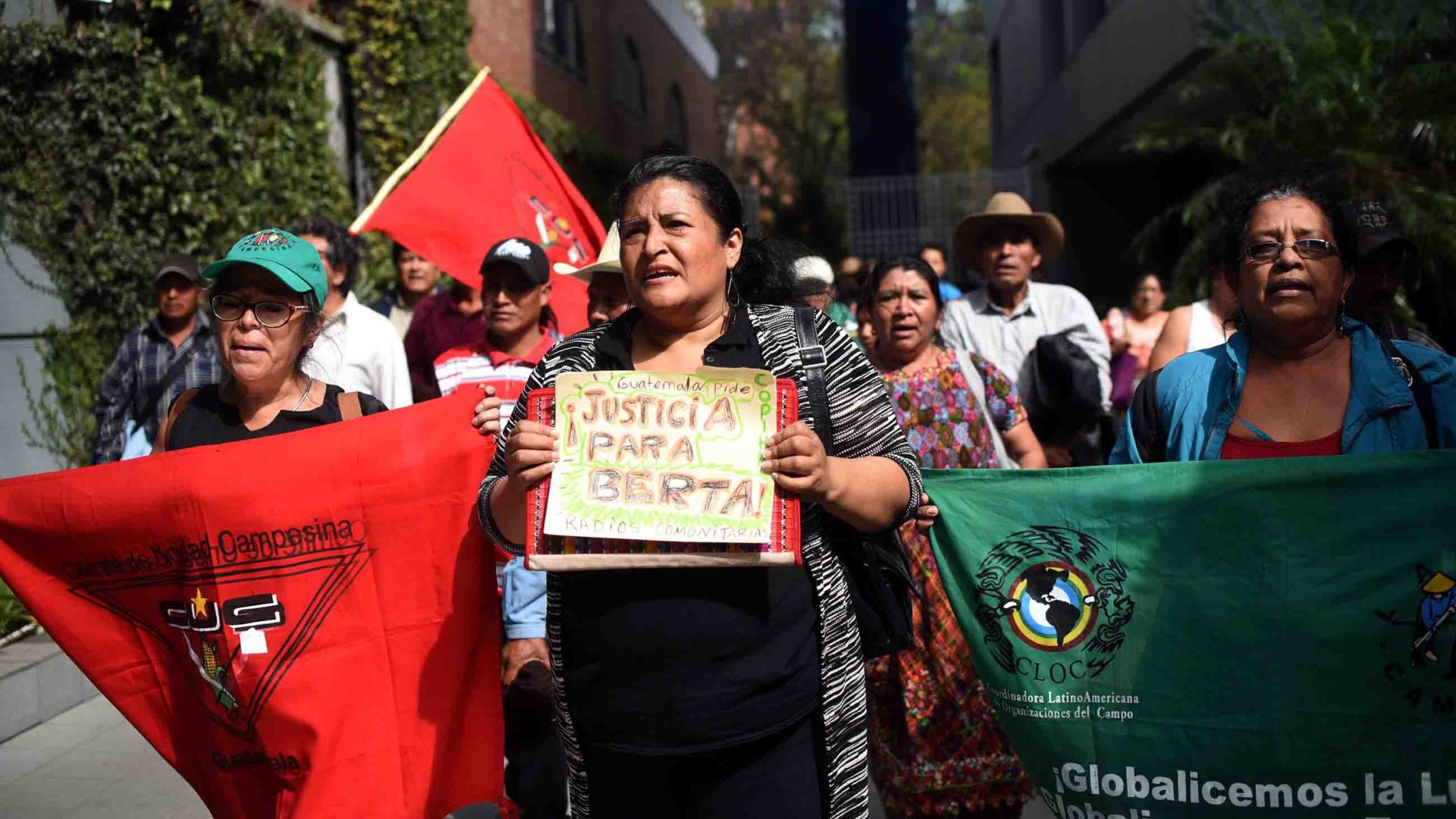
Since 2015, some 40 Indigenous people have been killed and dozens more injured and kidnapped in conflicts with settlers, according to the Center for Justice and Human Rights of the Atlantic Coast of Nicaragua. Nearly 3,000 Miskito people have fled their homes in the northern Caribbean region since 2015 due to conflict, according to a report by the Oakland Institute, a research nonprofit in California. So far this year, at least 10 Indigenous people have been killed and many have been injured in attacks by settlers. The Inter-American Commission on Human Rights recently called on the Nicaraguan government to “take immediate steps to prevent such acts [and] investigate and punish those responsible for them.”
The Nicaraguan Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources did not respond to repeated requests for comment.
Over the centuries, Indigenous and Kriol communities on the remote Caribbean coast have been subject to neglect and suppression by colonial and modern central governments. The region is home to around 135,000 Indigenous people from several groups and approximately 20,000 Kriol. While the federal government officially recognizes Indigenous and Kriol autonomous governments and communal land ownership, a long legal process to resolve land conflicts is incomplete, and settlers often take advantage of lax enforcement on the ground.
Becky McCray, a Rama attorney who works on behalf of Rama and Kriol communities in the Río San Juan Biosphere Reserve, says local communities have filed complaints with various state bodies including the police and Marena, detailing what she calls “a massive invasion” of the reserve and illegal activities like deforestation, slash and burn agriculture, and the logging of precious woods. Since 2018, she says, they have received no response from the government.
Settlers have forced Rama and Kriol families to leave homes and farming parcels on communal lands through displacement and threats of murder and sexual violence, McCray says. They often face food insecurity as they lose access to farming plots. The Rama and Kriol depend on natural resources for subsistence farming and fishing and water, as well as their health, she says.
McCray joined community leaders in a recent tour of their territory and witnessed significant new destruction: a road opening up a previously inaccessible area and large areas logged, burned, and cleared for agriculture.
“We’ve made every effort to convince them that in reality the reserve is at risk,” but the Nicaraguan government has done nothing, she says. Rama and Kriol communities have created their own patrols to document illegal settlement and other activities. They have also developed a community ranger program. But the remoteness of their posts can lead to greater vulnerability; McCray said that after one ranger’s family was attacked by settlers, the family decided to move, too frightened to pursue their case with the police.
Amaru Ruiz, president of Fundación del Río, an organization founded to preserve southeast Nicaragua, including the Río San Juan Biosphere Reserve, has documented churches, schools, and roads built illegally within the reserve. Ruiz attributes their presence to “municipal public policies to establish people within the reserve” carried out by local officials with tacit approval of the central government. He says these officials are among those profiting from the illegal sale of protected lands.
Ruiz, now living in Costa Rica, is one of the tens of thousands of dissidents who fled Nicaragua in 2018. After the government revoked its recognition of Fundación del Río as an organization that year, threats against him increased, he says. Most of Fundación’s members have been threatened, he says, and its radio and educational programs in Nicaragua have ceased. Recently, the caretaker of a small forest preserve owned by Fundación del Río was threatened by local authorities who want to take it over, Ruiz says.
Since 2012, Nicaragua has received nearly $6.5 million from the Forest Carbon Partnership Facility’s Readiness Fund, part of the U.N.-created, World Bank-funded program REDD+ (Reduce Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation) that provides funds for developing countries to create, and eventually implement, forest preservation plans. According to the Nicaraguan government, the country has carried out planning elements including training state agencies and holding “consultations” with Indigenous and Afro-descendant peoples, but needs an additional $5 million from the fund to finalize its plan. The minister for national policies, Paul Oquist, recently told a Nicaraguan climate change conference that the government’s fundamental strategy is forest preservation in the Caribbean region, which the government designated a critical “carbon capture zone” under its REDD+ program.
Yet Ruiz charges that the government’s participation in REDD+ is really about extracting resources under the guise of conservation. He says the Ortega government “has shown environmental concerns don’t interest them.” The Alliance of Indigenous and Afro-descendant Peoples of Nicaragua (APIAN) also criticized the program, saying the government has “promoted the advance of the agricultural and cattle ranching frontier through the forests that form part of our traditional territories” and fabricated “agreements” with Indigenous communities to comply with REDD+ requirements.
A World Bank spokesperson declined an interview request, but in a written response stated, “Nicaragua would have to reduce deforestation, reduce forest degradation, and increase reforestation at agreed rates to be able to receive any payment from the Carbon Fund” once its REDD+ plan is implemented. The program “benefits Indigenous and local communities, local governments, and others who manage the forest for emission reductions,” the statement continued.
In 2019, Miskito community leader Juan Carlos Ocampo brought a complaint of land invasion to government authorities, which they declined to investigate. “As a Nicaraguan, I have the right to the state’s protection and defense of my rights,” he says.
But for his part, Ocampo believes the struggle of Indigenous communities throughout Nicaragua “has the tools to succeed.” On the Caribbean coast, as throughout the country, he says, what they need is to recover the rule of law.
UPDATE:On September 27, 18 Rama and Kriol community leaders, including Rama attorney Becky McCray, were detained for several hours by the Nicaraguan army after completing a survey of illegal settlement and agriculture in protected areas of the Río San Juan Biosphere Reserve. The President of the Rama-Kriol territorial government was detained overnight and released on September 28.
Sara Van Note is a print and audio reporter based in New Mexico.