Out of Uganda: An Aggressive Crop Killer That Threatens Global Food
The video below is the first part in a six-part series examining the scourge of Ug99, a type of fungus that causes disease in wheat crops — one that scientists worry could threaten global food supplies. Visit our series archive for all published episodes.
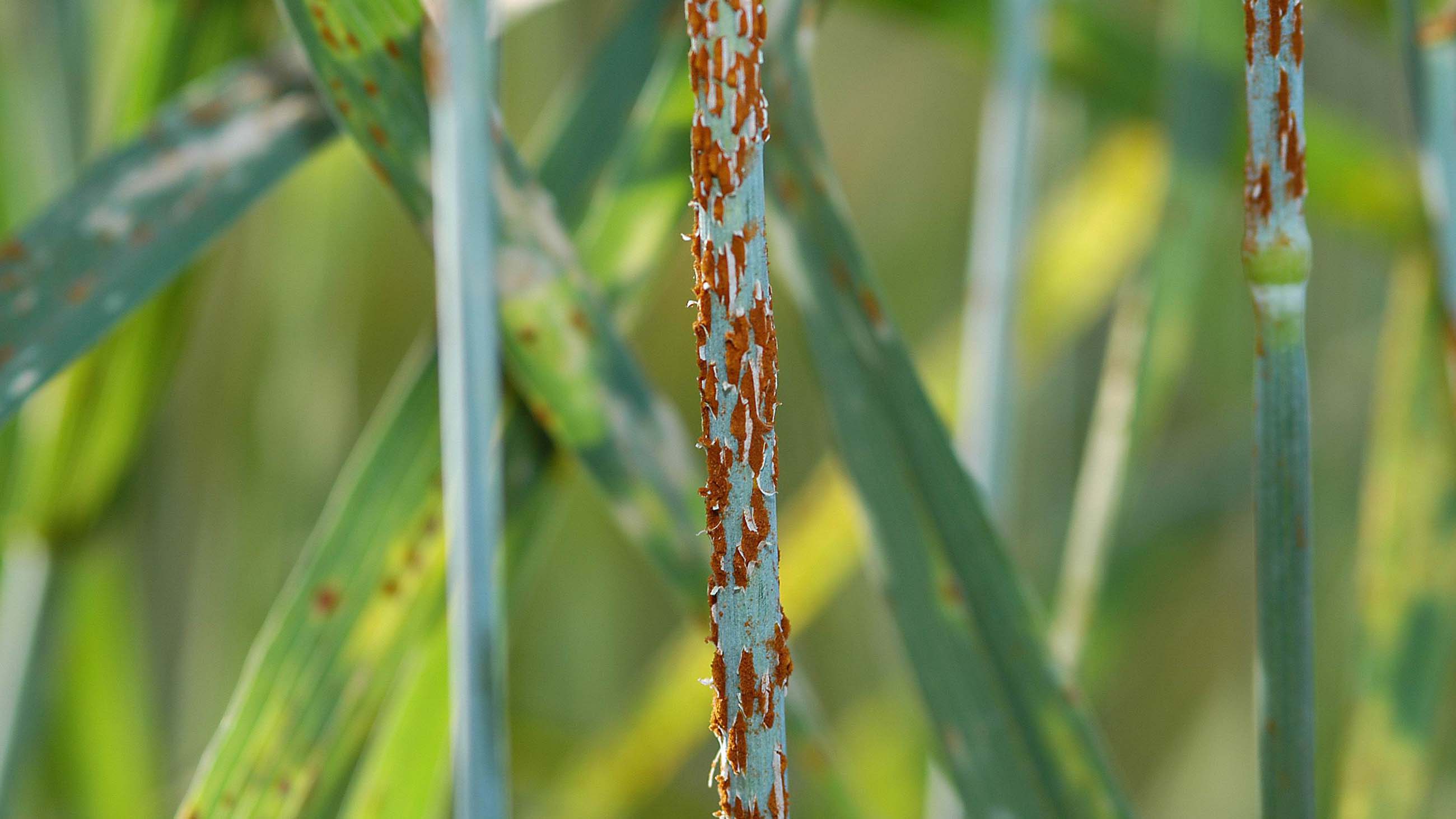
There was a time when one of the most dangerous crop diseases a wheat farmer could encounter in the field was stem rust. It is caused by a fungus, and its spores look like flecks of rust on metal — first red, later black in color. The fungus spreads along stems and leaves of cereal plants, consuming nutrients and causing the grains to shrivel.
Crops affected by stem rust are often entirely destroyed, and until the 1950s, the fungus was able to wreak havoc on agriculture across the globe — including in the United States. Researchers eventually managed to identify strong resistance genes against the fungus, and successfully bred those genes into new plant varieties beginning in the 1960s, leaving the fungus all but forgotten.
A generation later, however a new strain of wheat stem rust appeared — this time in Uganda in 1998. This new strain, which scientists called Ug99 (Ug for the country where it was first discovered, 99 for the year when it was officially named), was immune to most of the known resistance genes — and it remains a threat today. It is more aggressive than most known stem rusts, and it evolves far more quickly. Indeed, where there was only one strain in 1999, there are now at least 13 new pathotypes of Ug99, and they are spreading fast.
“Why Ug99 is important, first of all is, because it has virulence for many resistance genes,” says Julio Huerta, a wheat breeder and plant pathologist with the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center. “Second, it’s very aggressive. Extremely aggressive.”
“This is not a race that sleeps,” Huerta added. “That’s why we say rust never sleeps.”
Winds can carry the spores across borders, and scientists have now found Ug99 and its descendants throughout Eastern Africa, from South Africa to Egypt. Reports have also surfaced from Yemen and Iran, and the fungus probably won’t stop there.
Scientists worry that Ug99 will eventually spread further east and reach the wheat and barley breadbasket regions of India and China, and the consequences of this, they say, could be catastrophic — not only for local populations and economies, but for the world.
Continue to Part 2: A Precious Crop Under Threat
Kerstin Hoppenhaus and Sibylle Grunze are the founders of Hoppenhaus & Grunze Media, a Berlin-based film production studio specializing in documentary coverage of science.









Comments are automatically closed one year after article publication. Archived comments are below.
Monsanto’s Round Up [glyphosphates] can accelerate Fungus growth. In some places even though it’s not used to kill weeds it is sprayed on wheat to evenly “mature” the seed before harvest. The main purpose of newer GMO plant varieties was resistance to the weed spray so it would survive when sprayed. But the side effects are even more fungal infections on humans as well. The stuff is blown around in winds so it even gets into urban areas in agri-regions.
Applied Physics….The Law of Quantum Acoustics , expressed through mc3 = e3. All biological and Chemical Materials have a specific frequency…Gluon Negation. DARPA KNOWS THIS VERY WELL.
Please try V-Kure fungicide from Vanproz Agrovet , India.
It is working well on wheat rust.
http://Www.vanproz.com , you can buy online
I have reported about the research work by scientists at Bunginyanya Zonal Agricultural Research and Development Institute intensively. Varieties resistant to UG99 have already been released and farmers in Eastern Uganda and Western Kenya majoring in growing wheat are already growing these varieties. In one of my articles about Ug99 I had the opportunity of interviewing scientists carryout the same research in Cambridge UK at their the Jone Inns institute when I traveled to UK to attend a scientific meeting. In Uganda, the disease in no longer a major problem and I think with concerted research effort from Agricultural scientists in the globe the disease burden will be overcome
Any thing proven that can be done so far.
There is a company in Canada that has a new organic product that may kill this strain of fungus. It has been proven to kill club root which is very difficult to kill as well.